Vitamin D Blood Test: Measuring the Sunshine Vitamin for Bone, Immune, and Metabolic Health
The Vitamin D Blood Test, included in the PlexusDx Nutrition Deficiency Blood Test, measures 25-hydroxy vitamin D [25(OH)D], the most reliable indicator of vitamin D status. Often called the “sunshine vitamin,” vitamin D plays a crucial role in calcium and phosphorus absorption, supporting strong bones and teeth. But its impact goes far beyond bone health, influencing muscle performance, immune defense, cardiovascular balance, and metabolic function. Testing your vitamin D levels helps uncover deficiencies that may otherwise go unnoticed, allowing you to take proactive steps for long-term wellness.
What Is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that acts more like a hormone in the body. It can be produced naturally when your skin is exposed to sunlight, but it is also obtained through diet and supplements. Once in the body, vitamin D is converted into its circulating form, 25-hydroxy vitamin D [25(OH)D], which is measured in the blood. This form serves as the best indicator of total vitamin D availability and overall status.
Why Is Vitamin D Important?
Vitamin D has wide-ranging effects on health, including:
- Bone strength – Promotes calcium and phosphorus absorption, essential for building and maintaining strong bones and teeth.
- Muscle performance – Supports muscle contraction and reduces the risk of falls and fractures in older adults.
- Immune defense – Enhances immune cell function and helps regulate inflammation, reducing susceptibility to infections.
- Blood pressure and heart health – Plays a role in vascular tone and cardiovascular regulation.
- Insulin regulation – Supports glucose metabolism and healthy insulin sensitivity.
Because vitamin D influences so many systems, deficiencies may contribute to fatigue, frequent illness, bone pain, muscle weakness, and long-term risks such as osteoporosis or metabolic disease.
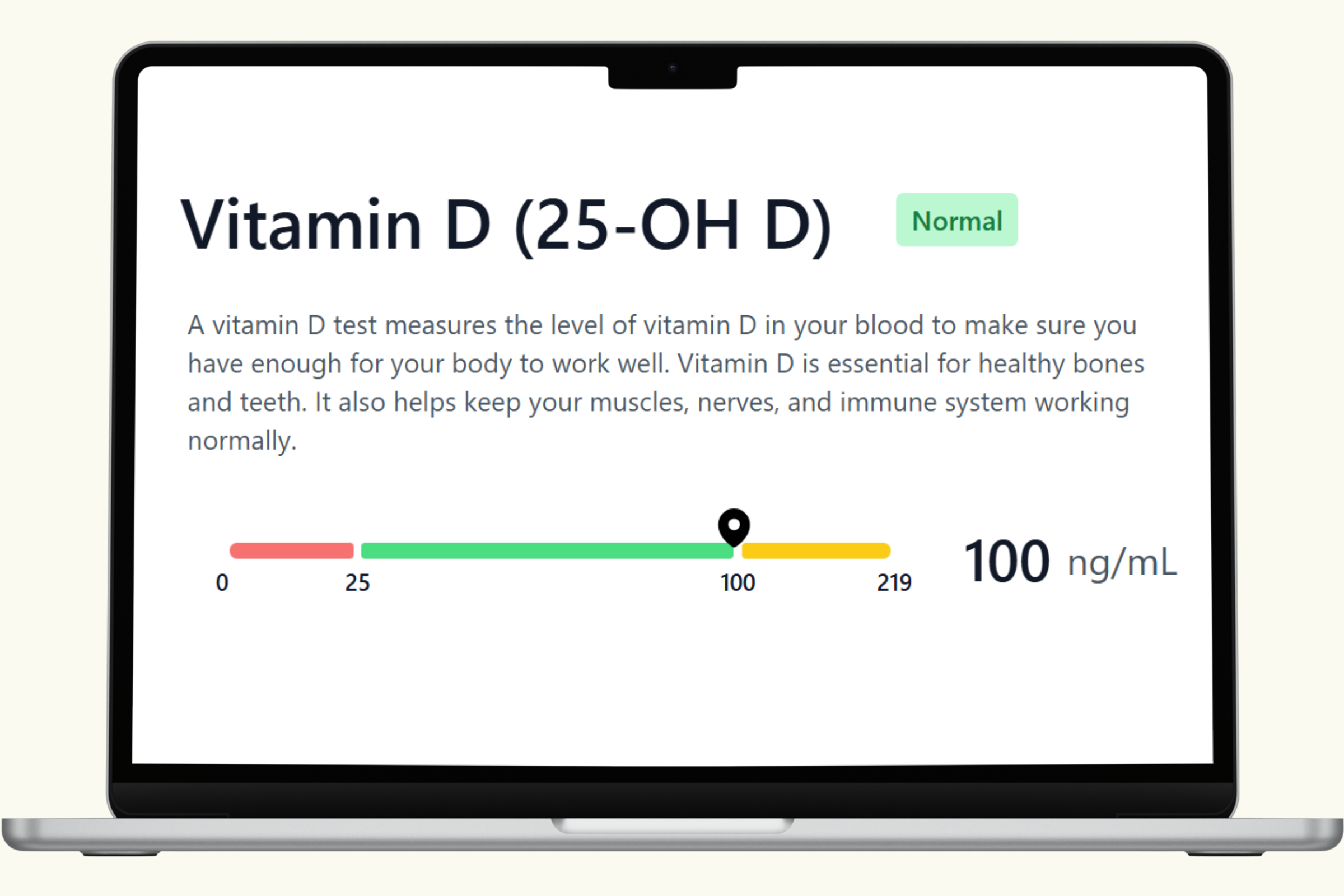
Vitamin D Blood Test Reference Ranges
Vitamin D is measured in nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL). Common reference ranges include:
- Deficient: < 20 ng/mL
- Insufficient: 20 – 29 ng/mL
- Sufficient: 30 – 100 ng/mL
- Functional/optimal range: 40 – 60 ng/mL (often cited as the range for optimal health and prevention of chronic disease)
- Potentially toxic: > 100 ng/mL
These ranges highlight that both deficiency and excess are possible, making regular testing important to maintain balance.
Who Is at Higher Risk for Vitamin D Deficiency?
Some groups are more likely to experience low vitamin D levels, including:
- Older adults – Reduced skin synthesis and dietary intake increase deficiency risk.
- People with darker skin – Higher melanin levels reduce the skin’s ability to produce vitamin D from sunlight.
- Individuals with obesity – Vitamin D can be sequestered in fat tissue, reducing its bioavailability.
- Vegans and vegetarians – Limited intake of animal-based vitamin D sources may lower levels without supplementation.
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women – Higher vitamin D needs to support maternal and infant health.
- People with limited sun exposure – Living in northern latitudes, wearing sunscreen, or spending most time indoors reduces vitamin D production.
Interpreting Low Vitamin D Levels
Low vitamin D levels may be linked with:
- Bone-related conditions: Rickets in children, osteomalacia in adults, and increased risk of osteoporosis.
- Immune challenges: Greater susceptibility to colds, flu, and other infections.
- Chronic disease risk: Associations with type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and certain autoimmune conditions.
- Musculoskeletal weakness: Fatigue, reduced muscle strength, and greater fall risk.
Interpreting High Vitamin D Levels
While deficiency is far more common, excess vitamin D from oversupplementation can cause problems. High levels may result in:
- Elevated blood calcium (hypercalcemia)
- Nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain
- Kidney stones or kidney damage in severe cases
For this reason, supplementing with vitamin D should be guided by test results, not guesswork.
At-Home Vitamin D Testing with PlexusDx
The PlexusDx Nutrition Deficiency Blood Test makes checking your vitamin D levels simple and convenient. With an at-home dried blood spot collection using an ADX card, you can test from the comfort of your home without the need for a lab appointment. Benefits include:
- Convenience – Easy finger-prick collection at home.
- Accuracy – Reliable measurement of 25(OH)D, the gold standard marker for vitamin D.
- Actionable insights – Helps guide dietary, lifestyle, and supplement choices.
How to Improve Vitamin D Levels Naturally
If your vitamin D levels are low, consider the following approaches:
- Sunlight exposure – Aim for 10–30 minutes of midday sun on bare skin a few times a week, depending on your skin type and location.
- Dietary sources – Include fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), fortified dairy or plant-based milk, and egg yolks.
- Supplements – Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is often recommended, especially in regions with low sun exposure, but dosage should be based on test results.
Who Should Consider a Vitamin D Test?
This test is beneficial for anyone, but especially for those who:
- Have limited sun exposure
- Follow a plant-based diet
- Experience frequent illness or fatigue
- Have bone pain, fractures, or muscle weakness
- Are pregnant, breastfeeding, or older adults
- Have chronic conditions such as diabetes, obesity, or autoimmune disorders
Take Charge of Your Health with PlexusDx
The Vitamin D Blood Test, part of the PlexusDx Nutrition Deficiency Blood Test, provides critical insight into one of the most common nutrient deficiencies worldwide. By measuring 25-hydroxy vitamin D [25(OH)D], you can identify whether your levels are optimal, deficient, or excessive. With at-home testing, you gain the power to monitor, adjust, and protect your health with confidence.
Order your PlexusDx Nutrition Deficiency Blood Test today and ensure your vitamin D levels support strong bones, resilient immunity, and lifelong wellness.
Share:
Vitamin B12 Blood Test