Blood Glucose Test
The Blood Glucose Test is one of the most widely used and important tests for understanding how well your body regulates sugar, or glucose, in the bloodstream. Glucose is the primary source of energy for your cells, and maintaining balanced levels is essential for metabolic health, brain function, and long-term vitality. This test plays a central role in identifying conditions like diabetes and prediabetes, as well as monitoring blood sugar in people already managing these conditions.
As part of the PlexusDx Diabetes & Heart Health Blood Test, blood glucose measurement can be performed easily at home using a dried blood spot (DBS) on an ADX card. This makes it simple to monitor your health without the need for a clinic visit, while still providing clinical-grade results.
What the Blood Glucose Test Measures
The test measures the amount of glucose circulating in your blood at a given moment. Since glucose levels fluctuate throughout the day depending on meals, stress, exercise, and hormones, doctors often use fasting glucose tests or pair them with other markers to better understand your body’s regulation of sugar.
- Fasting Blood Glucose: Taken after 8–12 hours without eating, this test shows your baseline glucose control without the influence of recent meals.
- Random Blood Glucose: Can be taken at any time of day to check for unusually high or low levels.
- Postprandial Blood Glucose: Measures how your body handles glucose after eating, often used to detect early metabolic problems.
Why Blood Glucose Testing is Important
Blood glucose testing provides essential insight into how well your body manages energy and can reveal hidden risks for serious health conditions. Chronically high glucose damages blood vessels, nerves, and organs, increasing the risk of diabetes complications, heart disease, kidney disease, and more. Low glucose levels, on the other hand, may cause dizziness, confusion, fainting, or even life-threatening emergencies if untreated.
By monitoring glucose, you can:
- Screen for diabetes and prediabetes
- Understand symptoms like fatigue, excessive thirst, frequent urination, or dizziness
- Evaluate how lifestyle and diet affect blood sugar
- Track progress in managing diabetes or other metabolic conditions
Reference and Functional Ranges
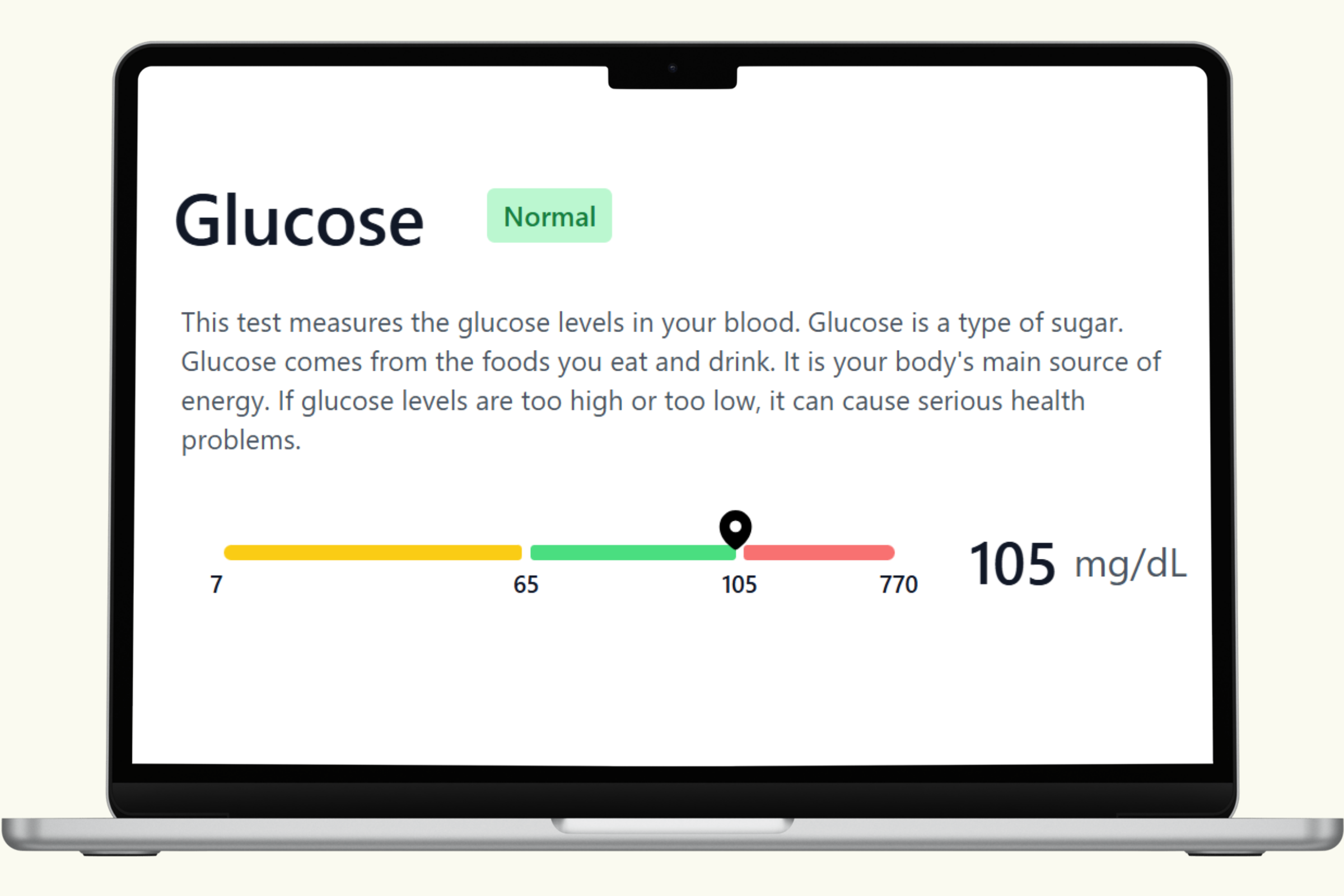
Commonly used blood glucose ranges include:
- Fasting Blood Glucose:
- Normal: 70–99 mg/dL
- Prediabetes: 100–125 mg/dL
- Diabetes: 126 mg/dL or higher on two separate tests
- Random Blood Glucose: Over 200 mg/dL with symptoms may suggest diabetes
Functional and preventive medicine often uses tighter “optimal” ranges for early detection:
- Fasting Optimal: 75–85 mg/dL
- Postprandial Optimal (2 hours after eating): Below 120 mg/dL
How the Test is Collected
The PlexusDx Diabetes & Heart Health Blood Test uses an at-home dried blood spot (DBS) collection method with an ADX card. After a simple finger prick, a few drops of blood are placed on the card, which is then mailed to the lab for analysis. This method is:
- Convenient and private
- Less invasive than a standard blood draw
- Clinically validated for accuracy
- Ideal for regular monitoring over time
What Can Influence Blood Glucose Levels?
Many factors affect your glucose levels on a daily basis:
- Diet: High intake of refined carbs and sugary foods can spike glucose, while fiber and protein help stabilize it.
- Physical activity: Exercise increases insulin sensitivity and helps regulate glucose more effectively.
- Weight: Excess body fat, especially around the abdomen, is linked with insulin resistance and higher glucose.
- Stress: Stress hormones like cortisol can raise blood sugar.
- Sleep: Poor sleep disrupts insulin regulation and glucose metabolism.
- Medications: Some drugs, such as steroids or diuretics, may affect glucose levels.
- Medical conditions: Diabetes, hormonal imbalances, and metabolic syndrome directly influence glucose regulation.
How to Improve Blood Glucose Control
Managing glucose often comes down to making sustainable lifestyle changes. Key strategies include:
- Balanced diet: Emphasize whole grains, lean protein, vegetables, and healthy fats while limiting refined sugars.
- Regular exercise: Aim for 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week, plus resistance training.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Even modest weight loss improves insulin sensitivity.
- Stress management: Mindfulness, breathing exercises, and yoga can reduce cortisol-driven glucose spikes.
- Consistent sleep: Aim for 7–9 hours of restorative sleep per night.
- Medical support: In some cases, medications such as metformin or insulin therapy may be needed under medical supervision.
Why Pair Glucose with Other Biomarkers?
While glucose is a critical marker, it is best interpreted alongside other tests. The PlexusDx Diabetes & Heart Health Blood Test also measures hemoglobin A1C, cholesterol ratios, triglycerides, and more. Together, these results give a more complete picture of metabolic and cardiovascular health, helping identify risks earlier and guide a personalized plan for wellness.
Take Charge of Your Health
The Blood Glucose Test is a simple yet powerful way to assess how well your body manages energy and to detect hidden metabolic issues. With PlexusDx at-home testing, you can measure and monitor your blood sugar levels conveniently, giving you the insights needed to take proactive steps toward better health. Whether you are screening for diabetes, managing prediabetes, or optimizing long-term wellness, this test provides the foundation for informed decision-making.
Share:
VLDL Blood Test
LDL-HDL Ratio Blood Test